
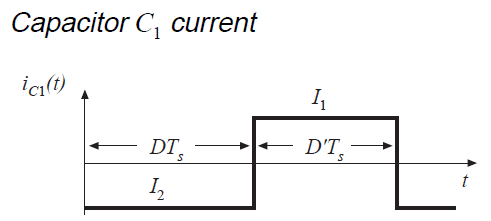
When the inductor current is always greater than zero, it is in CCM. It is worth noticing that any converters work in two distinct modes with respect to the inductor current: the continuous conduction mode (CCM) and discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). The building blocks of these converters are DC supply Vs, load, diode D, power electronics switch S, inductor L, and capacitor C. Basic circuit diagram of all the fundamental converters are shown in Figure 1. Similar analysis can also be done for the other types of converters. With the voltage and current relationship, influencing factors for the equilibrium of the converter such as the capacitor’s voltage ripple and inductor voltage-second balance condition have been derived. The four basic DC-DC converters considered for analysis are: Buck Converter, Boost converter, Buck-Boost Converter and Ćuk Converter. This technical article deals with the analysis of the four fundamental DC-DC converters (or choppers) in equilibrium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
